How to edit your Mac hosts file (Mac OS X) Sometimes you need to view a site on a development server. It’s something that I use regularly to connect to a development server using the regular site domain but mapped to a development server’s IP address. The hosts file is used to map domain names (hostnames) to IP addresses. It is a plain-text file used by all operating systems including, Linux, Windows, and macOS. The hosts file has priority over DNS. When you type in the domain name of a web site you want to visit, the domain name must be translated into its corresponding IP Address. Another way for editing hosts file on Mac is via apart from using Mac terminal text editor is TextEdit. Navigate to Finder Go Go to Folder Now type /private/etc/hosts and tap on Go. Copy the hosts file on your Mac’s desktop and then double click the file to make changes. If using the terminal you can use nano, vi, vim, emacs to edit the file. The only problem with some of these editors is finding an explicit line. As I seem to recall, the knownhost file message gives a line number. Since the lines in the knownhosts file are very long, a lot of these editors line wrap so just counting visible lines is not. Mac Hosts File Location. Since editing the hosts file is a risky task, Apple has intentionally placed it in a private folder on your system. That’s to prevent users from modifying it without proper knowledge and causing damage to the entire system.
HostsNews blog & Updates |
| Blocking Unwanted Connections with a Hosts File | ||||||||||
What it does ... You can use a modified HOSTS file to block ads, banners, 3rd party Cookies, 3rd party page counters, web bugs, and even most hijackers and possibly unwanted programs. This is accomplished by blocking the connection(s) that supplies these little gems. The Hosts file is loaded into memory (cache) at startup, so there is no need to turn on, adjust or change any settings with the exception of the DNS Client service (see below). Windows automatically looks for the existence of a HOSTS file and if found, checks the HOSTS file first for entries to the web page you just requested. The 0.0.0.0 (prefix) is considered the location of your computer, so when an entry listed in the MVPS HOSTS file is requested on a page you are viewing, your computer thinks 0.0.0.0 is the location of the file. When this file is not located it skips onto the next file and thus the ad server is blocked from loading the banner, Cookie, or some unscrupulous tracker, or javascript file. Example - the following entry 0.0.0.0 ad.doubleclick.net blocks all files supplied by that DoubleClick Server to the web page you are viewing. This also prevents the server from tracking your movements. Why? ... because in certain cases 'Ad Servers' like Doubleclick (and many others) will try silently to open a separate connection on the webpage you are viewing, record your movements then yes ... follow you to additional sites you may visit. Using a well designed HOSTS file can speed the loading of web pages by not having to wait for these ads, annoying banners, hit counters, etc. to load. This also helps to protect your Privacy and Security by blocking sites that may track your viewing habits, also known as 'click-thru tracking' or Data Miners. Simply using a HOSTS file is not a cure-all against all the dangers on the Internet, but it does provide another very effective 'Layer of Protection'. In case you're wondering ... this all happens in microseconds, which is much faster than trying to fetch a file from half way around the world. Another great feature of the HOSTS file is that it is a two-way file, meaning if some parasite does get into your system (usually bundled with other products) the culprit can not get out (call home) as long as the necessary entries exist. This is why it's important to keep your HOSTS file up to Date. Get notified of MVPS HOSTS updates. Special Note: new Windows 10 users ... the MVPS Hosts file installs just fine, no need to make any changes. Simply follow the instructions for Windows 10/8
Started providing a HOSTS file in 1998 ... and now celebrating 20 yrs. proudly still the #1 rated HOSTS file on Google ...
This download includes a simple batch file (mvps.bat) that will rename the existing HOSTS file to HOSTS.MVP then copy the included updated HOSTS file to the proper location. For more information please see the Windows version that applies to you ...
When you run the (mvps.bat) batch file - right-click and select: Run as Administrator. Once updated you should see another prompt that the task was completed. Some users may see a pop-up from certain Security programs about changes to the HOSTS file. Allow the change ... however if you see this pop-up (changes to the HOSTS file) at any other time ... investigate.
Reproduction of information on this site, in any form, is prohibited without express written permission.
Copyright © 1998 - 2020 All rights reserved. Active computer users are probably already familiar with the Hosts file that contains network information. Through this file you can block access from your computer to a particular website, or make other changes to the access of your computer to a certain IP address. Despite the fact that Mac Os is a system that is pretty much closed from user interference, it has a file named Hosts that can be edited. At the same time, editing here is not at all more difficult than on Windows, and within the framework of this article we will tell you how to do this. How to open and edit hosts via “terminal”Hosts File Mac Os XThe easiest way to access Host file editing is to use a command line, which in Mac OS is called “Terminal”. You can run “Terminal” utility through the Finder, it is located in the list of standard programs of the operating system, or you can just use a search and type its name. “Terminal” is running and now you need tostart editing the Host file. To do so you will need to enter and execute the following command: After activating this command, you will also need to enter the administrator’s password for the computer, because intervention in Hosts file is quite serious, and if this file is edited incorrectly, you may experience problems accessing certain websites on the Internet. After entering the right password, you will be able to see the Host file contents that can be edited by a user. When editing the file through “Terminal” your mouse will not work, so you will have to move between the lines of this file only with the help of your keyboard. Enter the changes you would like to make in the Hosts file. To save all changes in this file, you will need to press Ctrl + X on your keyboard. Next you are going to see a message asking you to confirm whether you want to change Hosts or no, confirm the action with “Y” button. How to open and edit hosts via finderThe second way to access Hosts and edit the file involves using the standard Finder. This way, you can open the Hosts file and edit it in any text editor, so this option may be preferable in a number of cases. To open Hosts through the Finder you need to right-click on the lower menu on the Finder and select “Go to Folder”. Then there will open a window and in this window you need to enter a path to the folder you want to go to. Enter the following address: And click “Go.” There will open a system folder in which the Hosts file is located. To start editing it, you need to right-click on it and select the editor that you would prefer to work with (you can use the standard TextEdit). In the window that opens, you can edit the Hosts file just like any other file in a text editor. But the Hosts system file is protected from editing. After you try to make changes to it, you will see a message with suggestion to create a duplicated file. Click “Duplicate”. After that the second file will form on the basis of the first one. Next, you will need to make all necessary changes to the new created file and save it in a convenient place, for example, on the desktop. When saving, select the .txt resolution (same resolution that the original Hosts file has). Now your new file is saved and you will need to just replace the old file in the system folder. To do this, drag the new file to the folder where the old Hosts is located and click “Replace” when the corresponding message appears. As a result of these actions, the old Hosts file will be deleted, and the new one will be used by the system instead. How to apply hosts file changesAdd Host Record To MacosSome changes that are made in the Hosts file are not perceived by the system at once and, accordingly, do not work. For the changes to take effect, you need to update the DNS cache. This can be done using the terminal with the command: 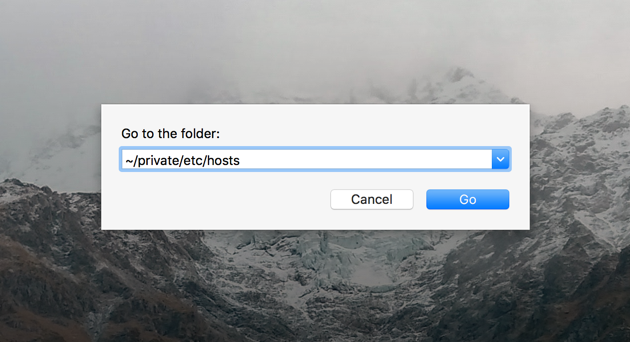 Hosts File Mac LocationAfter executing this command, the Hosts file will be read by the system again, and all the changes that were made to it will be reflected on the computer’s operation. |
Comments are closed.